Understanding Types of GST in India – CGST, SGST, and IGST
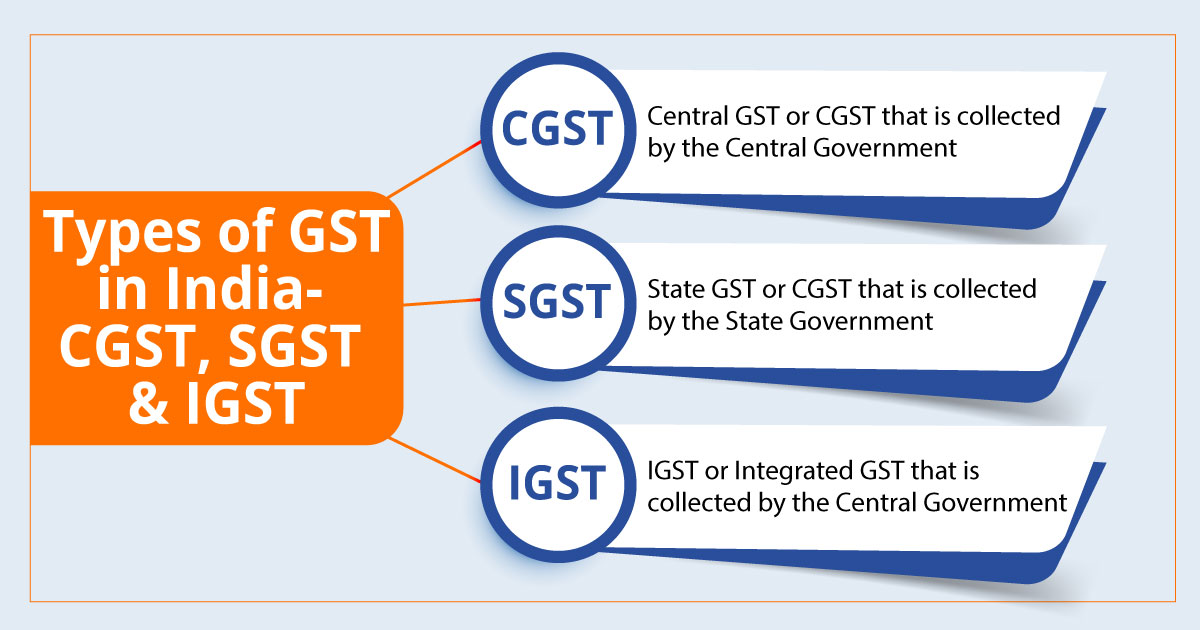
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive tax system applied across India. There are three main types of GST:
- CGST (Central GST): Collected by the Central Government on intra-state supplies, it is intended to replace various central taxes like service tax and central excise.
- SGST (State GST): Collected by State Governments on intra-state transactions, replacing various state taxes like VAT.
- IGST (Integrated GST): Levied on inter-state transactions and imported goods, it is managed by the Central Government but shared with states.
What is GST?
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a unified, multi-stage tax levied on goods and services in India. It replaces numerous indirect taxes like VAT, excise duty, and service tax, simplifying the country’s taxation system. GST is charged at each point of sale, with businesses receiving input tax credits for taxes paid on their purchases, thereby reducing the cascading effect.
A business can secure financing for its operations through various means, including a business loan, working capital loan, MSME loan, or a Mudra loan, each offering distinct support to small and medium enterprises.
Replaced Taxes with GST
The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has revolutionized India’s taxation system, consolidating multiple taxes into a single, unified framework. Here’s a detailed look at the various taxes replaced by GST:
- Central Taxes:
- Service Tax: This was a tax levied on services. GST integrates it into its structure, with service providers now collecting GST instead.
- Central Excise: This tax was levied on the production and sale of goods. GST replaces it, and goods are now taxed under the GST system at various rates depending on the product category.
- Central Sales Tax (CST): Levied on inter-state sales of goods, this tax is now covered under IGST (Integrated GST), making the process seamless for businesses engaging in interstate trade.
- State Taxes:
- Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT was levied by individual states on intra-state sales of goods. GST’s dual structure (CGST and SGST) replaces VAT, with both the Central and State Governments sharing tax revenue from intrastate transactions.
- Entry Tax: This was a tax levied by some states on the entry of goods. GST eliminates this tax, streamlining the flow of goods across states.
- Luxury Tax: This was imposed on luxury goods and services by various states. Under GST, these items are taxed at higher GST rates, reducing the need for a separate luxury tax.
- Entertainment Tax: Levied by states on activities like movies and events, GST replaces this tax for all activities except those levied by local bodies, integrating entertainment into the GST framework.
- Other Taxes:
- Octroi: This was a tax imposed by local municipalities on goods entering a city. GST removes this tax, streamlining goods movement across regions.
- Purchase Tax: Previously levied on specific goods by certain states, GST’s comprehensive framework includes these goods within its tax structure.
How To Register For ICEGATE?
Registering for ICEGATE (Indian Customs Electronic Gateway) is crucial for businesses engaged in import-export activities in India. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Visit the ICEGATE Website: Go to the official ICEGATE website to start the registration process.
- Select “New Registration”: Click on the “New Registration” button to begin your registration.
- Choose a User Type: ICEGATE offers various user types, including Importer, Exporter, CHA (Customs House Agent), and others. Select the appropriate category.
- Fill in Details: Enter all required details, such as business information, PAN number, email, and contact information. Make sure all data is accurate and up to date.
- Upload Documents: Provide necessary documentation, including your PAN card, GST registration certificate, and business license.
- Set Username and Password: Create a secure username and password, ensuring they meet ICEGATE’s security requirements.
- Verification: After submitting the form, ICEGATE will send a verification email. Click the link to verify your registration.
- Confirmation: Once verified, you will receive confirmation of successful registration. You can now log in to ICEGATE using your credentials.
- Access Services: After logging in, you can access various services, including filing documents, tracking shipments, and managing customs transactions.
How Many GST Tax Types Are There?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India is designed to streamline the tax system by consolidating multiple indirect taxes. The GST framework is structured based on the nature of the transactions, either interstate or intrastate. The tax levied differs depending on whether the transaction occurs within one state or across state boundaries.
- Inter-State Transactions
Interstate transactions refer to transactions that occur between two different states. When goods or services are supplied to another, the GST collected is divided between the Central Government and the State Government where the goods or services are consumed. For example, if a supplier in Jharkhand sends iron ore to a customer in West Bengal, the tax collected from the sale will be shared between the Central Government and the West Bengal State Government, as the destinate state.
- Intra-State Transactions
Intrastate transactions occur when the sale or supply of goods and services happens within the same state. In such cases, the GST collected is divided between the Central Government and the State Government of the concerned state. For instance, if a business in Jharkhand supplies iron ore to a customer within Jharkhand itself, the GST collected will be divided between the Central Government and the Jharkhand State Government.
Different Type of Tax
The three different type of GST tax in India include:
- What is CGST (Central GST):
- Definition: The central goods and service tax is collected by the Central Government on intra-state transactions of goods and services.
- Purpose: It replaces various central taxes, including service tax and central excise duty, streamlining the central taxation system.
- Revenue Sharing: The revenue collected goes directly to the Central Government.
- What is SGST (State GST):
- Definition: SGST stands for state goods and services tax. It is Levied by individual states on intra-state transactions, SGST replaces various state taxes like VAT and entry tax.
- Revenue Sharing: The revenue collected from SGST goes directly to the State Government where the transaction occurred.
- What is IGST IGST (Integrated GST):
- Definition: IGST stands for integrated goods and services tax. It is applied to inter-state transactions and imports, IGST simplifies taxation for cross-border activities.
- Collection: The tax is collected by the Central Government, which then distributes it between the Central and State Governments according to predetermined formulas.
- Purpose: It replaces the previous Central Sales Tax (CST) and simplifies the taxation of goods and services crossing state borders.

Components of GST
| Component | Description | Collection & Sharing |
| CGST (Central GST) | Levied by the Central Government on intra-state transactions of goods and services. | The revenue goes directly to the Central Government, replacing various central taxes, such as service tax and central excise duty. |
| SGST (State GST) | Levied by State Governments on intra-state transactions. | The revenue goes to the respective State Governments, replacing various state taxes like VAT and entry tax. |
| IGST (Integrated GST) | Applied to inter-state transactions and imports. | Collected by the Central Government and shared between the Central and State Governments according to predetermined formulas. It replaces the previous Central Sales Tax (CST). |
Current Application of the Different Types of GST
| GST Component | Application |
| CGST (Central GST) | Applied to intrastate transactions of goods and services, collected by the Central Government. |
| SGST (State GST) | Levied by State Governments on intra-state transactions. |
| IGST (Integrated GST) | Applied to inter-state transactions and imports. |
Difference Between the Types of GST
| GST Component | Definition | Application | Recent Updates |
| CGST (Central GST) | Levied by the Central Government on intra-state transactions. | Replaces various central taxes like service tax and central excise duty. | Discussions are ongoing to revise CGST rates on select goods and services to balance fiscal deficits. The Central Government has also intensified compliance drives to ensure accurate reporting. |
| SGST(State GST) | Levied by State Governments on intra-state transactions. | Replaces various state taxes like VAT and entry tax. | States are focusing on streamlining SGST compliance, particularly in sectors like e-commerce and real estate, while also working with the Centre on potential rate revisions. |
| IGST (Integrated GST) | Levied on inter-state transactions and imports. | Replaces the Central Sales Tax (CST), simplifying taxation on inter-state and international transactions. | Efforts are underway to expedite IGST refunds for exporters and simplify the inter-state revenue-sharing mechanism. |
Who is Liable to Pay GST?
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is applicable to a broad range of entities engaged in the supply of goods and services. Here’s a concise overview of who is liable to pay GST:
- Businesses: All businesses that supply goods or services and have an annual turnover exceeding ₹40 lakh (₹20 lakh for special category states) are liable to register and pay GST.
- Individuals: Freelancers, consultants, and service providers are also subject to GST if their annual income exceeds the threshold.
- Consumers: GST is a consumption tax, meaning the end consumers bear the final tax burden, with businesses passing on the GST cost to their customers.
- Other Entities: Importers, exporters, and e-commerce companies are also subject to GST regulations.
Goods Exempted from GST Payment
| Goods | Description | Recent Updates |
| Basic Food Items | Items such as rice, wheat, and pulses are exempted from GST, ensuring affordability for essential food staples. | The Indian government recently reinforced this exemption to alleviate the cost of living for low-income families. |
| Healthcare Products | Medicines, vaccines, and essential healthcare items are largely GST-exempt or taxed at a reduced rate. | New exemptions and tax reductions on specific medical equipment have been announced, especially those related to COVID-19. |
| Books | Educational books, including textbooks and reference materials, are GST-exempt. | Discussions are ongoing to ensure the continued exemption of educational materials, contributing to accessible education. |
| Agricultural Equipment | Certain agricultural tools and equipment, like hand tools and fertilizers, are exempted from GST. | The government recently announced support for the agriculture sector, emphasizing tax benefits for key inputs. |
| Handicrafts and Traditional Products | Items crafted by traditional artisans, such as handloom textiles and pottery, may be GST-exempt or taxed at a lower rate. | New exemptions have been announced to protect the livelihoods of local artisans and promote traditional crafts. |
Conclusion
GST has simplified the taxation system in India by unifying various indirect taxes under a single framework. It benefits businesses and consumers alike. The three types of GST- SGST, CGST and IGST play a crucial role in ensuring smooth transactions within states and across borders. With streamlined tax collection and easier compliance, businesses can focus on growth and expansion. For businesses seeking financial support amidst this tax transition, platforms like Lendingkart offer tailored financing options to help manage working capital and foster business growth efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 4 types of GST in India?
- CGST: Central GST, levied by the Central Government on intra-state transactions.
- SGST: State GST, levied by State Governments on intra-state transactions.
- IGST: Integrated GST, levied on inter-state and import transactions.
- UTGST: Union Territory GST, applicable to transactions in union territories.
2. What are the 5 types of GST rate?
- 0%: For essential items like basic foodstuffs.
- 5%: For goods and services like packaged food and books.
- 12%: For mid-range goods and services, such as processed foods.
- 18%: For standard items, including electronic goods.
- 28%: For luxury goods and services, including automobiles.
3. What are the 3 types of GST registration?
- Regular Registration: For businesses exceeding the annual turnover threshold.
- Composition Scheme: For small businesses with turnovers below a certain limit, offering simplified compliance.
- Casual Taxable Person: For entities with occasional business activities in India, requiring temporary registration.
4. What is IGST?
- IGST (Integrated GST) is levied on inter-state transactions and imports. It simplifies the taxation of goods and services moving across state borders, replacing the Central Sales Tax (CST). The Central Government collects IGST and distributes it between the Centre and states according to predetermined formulas.




 NOTE: No processing fees are being charged by Lendingkart before disbursement of the loan amount. Any individual claiming otherwise must not be entertained. Please report such activity on
NOTE: No processing fees are being charged by Lendingkart before disbursement of the loan amount. Any individual claiming otherwise must not be entertained. Please report such activity on 